At CLEIO, we deeply understand this. When it comes to developing software for medical devices, testing is an integral step in our process. It ensures that the software not only meets user needs but also complies with regulatory standards.
Why Software Testing Matters
Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Medical devices are subject to rigorous international standards that guarantee their effectiveness and the safety of patients and their data.
Software testing helps to demonstrate compliance with these standards by verifying that risk management requirements are met.
Enhancing Reliability and Performance
Testing identifies and rectifies bugs and defects that could compromise the reliability and performance of medical devices under various conditions.
Mitigating Risks
By detecting potential issues early in development, software testing reduces the risk of errors before launching the product to the market.
This approach helps prevent incidents that could harm patients, lead to product recalls, litigation, and damage to the manufacturer’s reputation (including use-related risks, data breaches, and incorrect results).
Continuous Improvement and Innovation
Software testing is invaluable for product improvement. It provides insights into user experience and helps identify potential enhancements or new needs.
The Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC)
Contrary to popular belief, software testing isn’t a one-time event. It’s a series of activities following a methodical approach. The STLC guides teams through the various stages of software testing, from planning to closure.
Integrated with the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), the STLC ensures that testing isn’t an afterthought but an inseparable part of the development process.
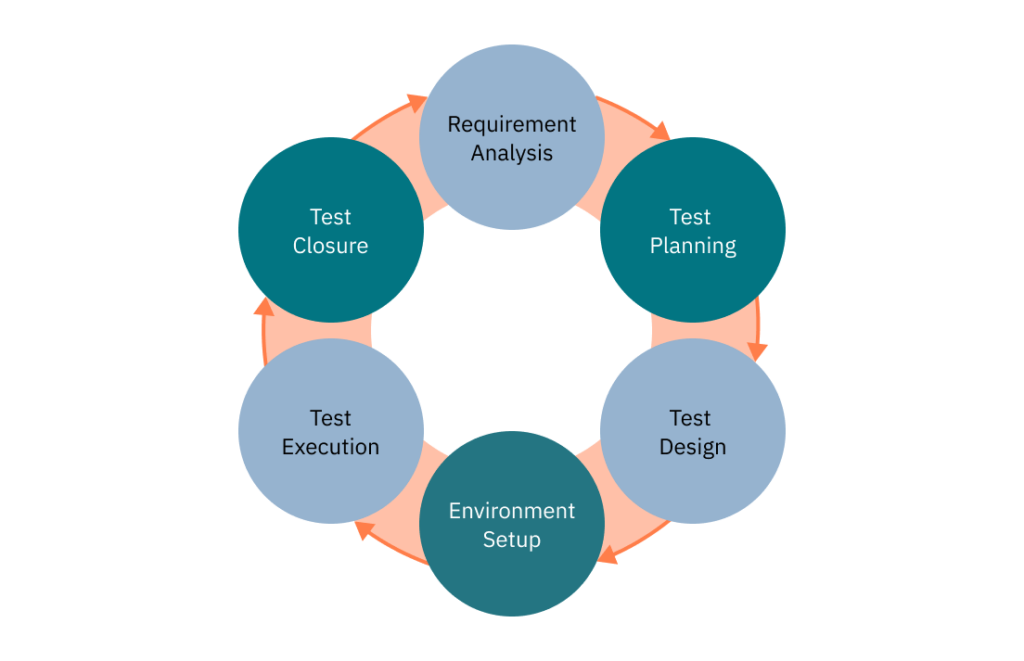
Here are the six key steps of the STLC:
Requirement Analysis
This essential phase involves a thorough evaluation of requirements to pinpoint testable elements and define appropriate testing methods. This ensures complete test coverage.
Test Planning
Informed by the earlier requirement analysis, the test plan defines testing objectives, methods, and schedule. This phase also includes resource allocation, role designation, and tool selection.
Test Design
The test design phase involves creating detailed test cases and defining acceptance criteria for each feature. This requires a thorough understanding of the software requirements and the risks associated with its medical use.
Test Environment Setup
The test environment must mirror the real-life conditions under which the software will be used. This may involve setting up specific medical equipment, secure data servers, and communication networks. The configuration must ensure tests are representative, reliable, and reproducible.
Test Execution
Tests are executed according to prepared test cases, and the results are meticulously recorded and analyzed. This phase is essential for identifying defects, bugs, and deviations from requirements.
Test Closure
Test closure evaluates the effectiveness of the testing process and documents lessons learned for future projects. It includes writing detailed test reports that can be used for regulatory certification and software validation. This stage ensures all test objectives have been met and the software is ready for production.
Types of Software Testing
Unit Testing
Unit tests focus on the smallest software components, such as functions or procedures. Often automated and conducted by developers themselves, these tests aim to verify that these components function correctly in isolation.
Integration Testing
Following unit testing, integration testing evaluates how different parts of the software work together. It’s crucial for detecting interface issues between modules.
System Testing
This step tests the entire software to ensure it meets all specified requirements. It evaluates performance, reliability, and compatibility in an environment simulating actual use.
User Acceptance Testing
User acceptance testing allows end-users to validate the software under real-life conditions. It’s a key step in ensuring the software meets their expectations and is ready for deployment.
Regression Testing
Regression testing ensures new modifications don’t introduce new bugs into existing parts of the software. It is particularly important in agile development environments where updates are frequent.

Benefits of Software Testing
Maintaining High-Quality Standards
Software testing ensures the final product meets the highest quality standards, which are essential in the medical field. For example, rigorously tested patient record management software guarantees accurate and secure handling of patient information.
Reducing Costs by Identifying Problems Early
Identifying and fixing defects early in development is far less costly than resolving them after the product launch. It also avoids the costs associated with product recalls, legal litigation, and damage to the company’s reputation.
Increasing Customer Satisfaction
A flawlessly functioning medical device enhances the user experience and confidence in the product. This can lead to better treatment adherence and, ultimately, better health outcomes for patients.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Thorough testing facilitates compliance with regulations and standards, a crucial aspect of obtaining the necessary approvals for market launch. This is especially important in the medical context, where regulatory requirements can evolve rapidly.
By adopting a structured software testing life cycle, and conducting tests adapted to each phase of development, developers ensure they meet not only regulatory requirements but also the expectations of end-users.
Therefore, testing is an essential investment in fostering innovation, while guaranteeing the quality, safety, and compliance of products brought to market.